Planning
Planning scans
Radiology or radiography is the term used to describe the diagnostic imaging that is used to reveal, diagnose or examine cancers. The machines used for diagnostic purposes are also used for radiation therapy planning purposes.
Computer tomography (CT), Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans are all three dimensional and most commonly used at ARO.
ARO can also use four-dimensional computed tomography (4DCT) which records movement or change in position due to the natural functions of your body. This is particularly important information for planning and then treating cancers near organs like your heart or lungs.
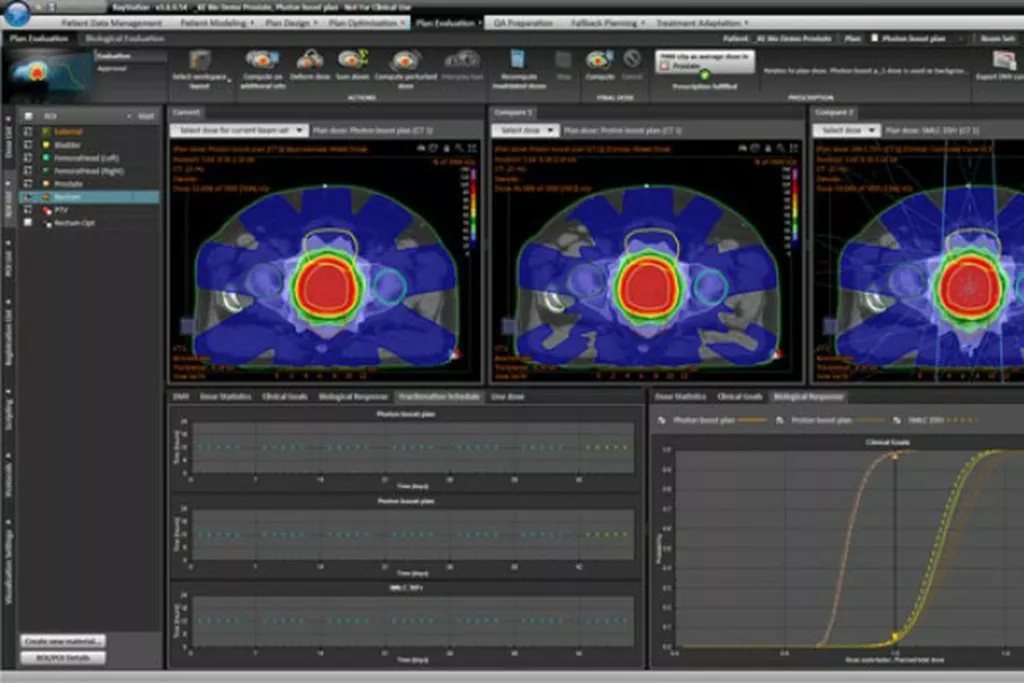
Patients are scanned in their treatment position and these dedicated images are then transferred to RayStation, the ARO computer planning system. Radiation therapy planning is a complex process involving a radiation oncologist, radiation therapist and physicist who work together to create an individualised treatment plan.
RayStation has the tools to shape the radiation to match the identified target on the planning images and gives a visual illustration of dose. We can see how radiation therapy will be delivered each fraction (session) and what side effects can be anticipated before treatment is starts.
Image Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT)
Image guided radiation therapy (IGRT) refers to a variety of 2D, 3D and 4D imaging techniques during the course of treatment. Images are taken when the patient is in position, immediately before (and sometimes during) each treatment so radiation therapists can see exactly where a target is and if necessary how it is moving. These images are overlaid with the planning images and if necessary patient position can be adjusted to ensure radiation is delivered to the exact place as intended.
IGRT gives confidence to shape radiation treatment more precisely to the target area. Margins around the target area can be small, side effects minimised and higher doses can be delivered safely. Different parts of the body can tolerate different amounts of radiation so IGRT also makes it possible to treat cancers that were hard to access in the past.
IGRT guides daily treatment and also helps identify when a treatment plan may need modifying such as when the target has reduced in size or the patient has had significant weight change. In some situations patients may need to have another planning scan.
Surface Guided Radiation Therapy (SGRT)
Exactrac dynamic image guidance combines both thermal for real-time surface tracking and the X-ray imaging for internal anatomy. It is very advanced using 300 000 surface points and specific immobilisation equipment.
Understanding Your Treatment
The Patient Pathway
We understand you may be anxious about having radiation therapy. Read about the patient pathway and what to expect before, during and after radiation therapy treatment. AT ARO we work closely with your radiation oncologist to develop an individualised treatment plan for each patient.
Explore the patient pathway